Email 101
December 2016
Choosing an email provider
Some features to consider when choosing a provider:
Price
Storage space
Ease of use
Attachment size limitations
Access from relevant platforms (desktop, Web, mobile)
Other, integrated services (calendar, travel planner, social networking, and so forth)
There literally are a hundred or more providers from which you can choose.
And, yes … you can choose more than one.
In fact, some providers require that you have a second email provider so that the alternate address can be used as a “rescue” line!
Your best bet in choosing an email provider is to visit their websites, read online reviews, and compare services provided to meet your needs.
Some of the more popular providers; all provide both free and premium services.
Zoho Mail
Outlook.com (Microsoft) – If you’ve been using this a long time, your email address may end with hotmail.com or live.com.
Gmail (Google)
Yahoo Mail (Yahoo!)
ProtonMail – email is encrypted.
iCloud Mail (Apple)
Good or bad email?
Bad emails commonly are known as spam.
Good emails commonly are known as ham.
Spoofed emails are those messages that come from a forged sender address.
Phishing emails are spoofed emails that appear to come from a legitimate business in order to trick the recipient into sharing his/her personal (and usually financial) information.
Email clients
An email client is a program that you use to access and manage your email.
There are three basic types of clients:
Desktop clients – Programs run on desktop and notebook computers.
Client apps – Programs run on mobile devices.
Webmail clients – Accessed as a webpage through a browser on desktops, notebooks, and mobile devices.
Webmail clients are the easiest to access.
Pros:
They require no extra software installation.
You can access your email from any device with a browser (even your smart TV).
Cons:
If you have multiple email accounts, you must visit a different webpage for each account.
Desktop clients and apps generally provide more options.
Pros:
They let you manage multiple email accounts.
Cons:
They must be installed and set up, so you cannot easily move between computers.
Some of the more popular desktop/app clients:
Outlook (Microsoft)
Thunderbird (Mozilla)
Mailbird
Zimbra
Opera
Inky – A client that encrypts your email.
POP3 vs IMAP vs Exchange
When installing an email client program or app, you may be asked to choose between POP3, IMAP, and Exchange.
These are different protocols for accessing email.
Exchange is the protocol used by email servers running the Microsoft Exchange program.
If you have an OSU email address, this is the protocol you will use.
The POP3 and IMAP protocols are used on other mail servers.
Generally, IMAP is recommended when you want the ability to check your email from multiple devices.
A local copy of the email is made, but the original stays on the server.
POP3 is a better choice if you read your emails on a single device and have limited bandwidth.
Emails are downloaded to the local client, and then the original is deleted.
Encryption and signing
Encryption of a message provides security, but only works if the recipient can decrypt the message.
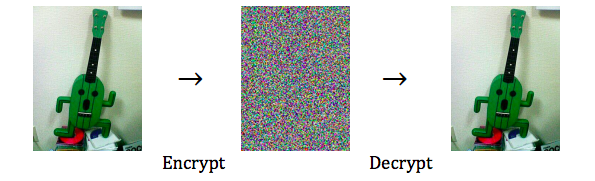
Digital signing permits the sender to “sign” an email in such a way that the recipient can be assured that it came from the purported sender (or someone who has the sender’s private signing key).
Demos and questions
Let’s take a look at email access via webmail clients and desktop programs.
